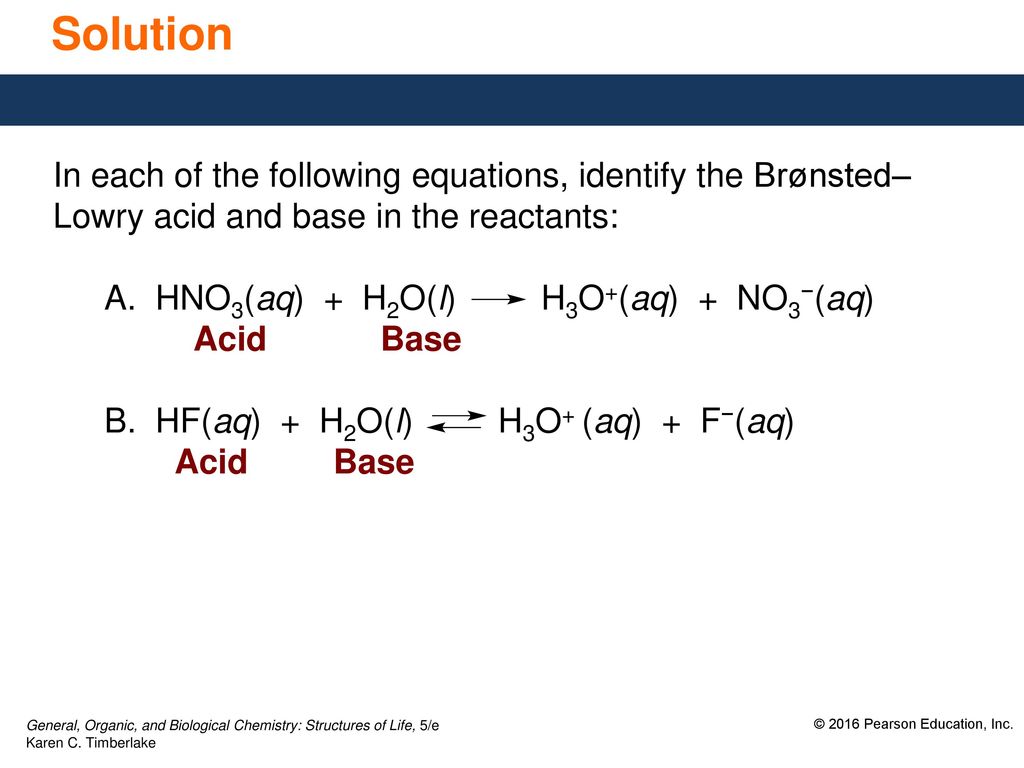
According to the Bronsted-Lowry model an acid is a proton donor and a bas Add To Playlist Add to Existing Playlist. Identify the Bronsted Lowry acid in the following reaction H2O CO 2 3 HCO 3 OHA from CHEMISTRY 1305 at University of Texas El Paso.

Recognizing Bronsted Lowry Acids And Bases Youtube
Lets answer the brown said Laurie Acid and base in the reaction given.
. Write the Bronsted-Lowry reactions in aqueous solutions of the following substance. In the above reaction reactant A A l H 2 O 6 3 loses one proton from one H 2 O and formed product C A l H 2 O 5 O H 2. Now we can find the pH.
This will be our Proton donor and our brown said Lowry Base will be an H three which be your proton except ER for B were toe. Identify the Brønsted-Lowry acids in the following reaction. H 2 C O 3 HC O 3 - H.
Create a New Plyalist. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. For each of the following reactions identify the Bronsted-Lowry acids and b 0631.
H2O CO3 2- aq. _ Defining Acids Bases Part A. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
How to Identify Bronsted-Lowry Acids. 2-logH3O ------H3O10 x 10-2. H Cl H 2O Cl H 3O.
Identify the given chemical equation. Who are the experts. 5 Acids Bases Acid Base Reactionpdf.
H2O l HCO31- aq H3O aq CO32- aq. H 3 PO 4 aq H 2 O l H 2 PO 42 aq H 3 O aq A. HC O 3 - H H 2 C O 3.
Thus B and D form another conjugate pair. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Identify the Lewis acid and Louis space.
The hydrochloric acid drops the hydrogen proton while water picks it up. Write the forward and backward ionic equations separately. Therefore is acting as a Brønsted-Lowry acid.
Predict whether the substance will behave as an acid or a base. A Bronsted-Lowry acid is a substance that donates a proton in the form of a hydrogen ion. In this reaction donates a proton to water.
Thus we can conclude that the products formed in this Bronsted. A HCl NH3 NH4 Cl- b HSO4-. POH-logOH ---- pOH-log1x10-12 -----pOH12.
So D is a Bronsted-Lowry acid. A l H 2 O 6 3 H C O 3 A l H 2 O 5 O H 2 H 2 C O 3 A B C D. For example ammonia and hydrogen chloride may react to form solid ammonium chloride according to the following reaction.
Learn more about BrønstedLowry acid-base theory here. Thus is the conjugate base of. According to Bronsted-Lowry acids are the species which donate hydrogen ions to another specie in a chemical reaction.
The one LOSING H is the acid thats the one DONATING the proton. B HBr H2O H3O Br HBr H 2 O H 3 O Br. H2O CO32- HCO3- OH-asked Jan 27 2020 in Chemistry by Pedro.
2 The compound H2CO3 is both a strong acid and a diprotic acid. So for a the brown said Lowry acid will be each X. When water accepts a proton is formed.
BRONSTED LOWRY ACIDS BASES WORKSHEET According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a proton H1 donor and a base is a proton acceptor. Some other concepts for acids and bases are Arrhenius concept and Lewis concept. Bronsted Lowry acid is that reactant in a reaction that loses proton and it is accepted by bronsted base.
152 Identify the Bronsted-Lowry acid in the following reaction. Solution for Identify the Bronsted Lowry Acid and Bronsted Lowry Base and their conjugate pairs in each reaction. Identify and label the Brønsted-Lowry acid its conjugate base the Brønsted-Lowry base and its conjugate acid in each of the following equations.
3 The pH of a solution with OH- 1 X 10-8 is. Hence option B Is correct. Bases are the species which accept a hydrogen ion upon chemical reaction.
HCO3 - aq OH- aq a. Now we can use the pH-logH3O to find the hydrogen ion concentration. Identify the Bronsted-Lowry acid in the following reaction.
The one GAINING H is the base thats the one ACCEPTING the proton. In the reaction Faq H₂Ol HFaq OHaq H₂O is a BrønstedLowry acid and F a BrønstedLowry base. For example in the reaction.
After donates its proton the ion is formed. C HS H2O H2S OH HS H 2 O H 2 S OH. Formation of a coordinate covalent bond is always part of a Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction.
Write the Bronsted-Lowry reactions in bartleby. Bronsted-Lowry theory states that an acid is a molecule that drops H ions protons and a base picks them up again. For example Here the products formed in this Bronsted-Lowry reaction are and.
The Bronsted-Lowry base in turn accepts this proton and the resulting products are a conjugate acid and. The Arrhenius definition- supply the correct products or write the complete equation and identify the compound that produces the Arrhenius acid or base. H2O l BH2PO42- aq CH3PO4 aq DH3O aq Expert Answer.
So the Lewis acid is theorem Tron Pere except ER which. Identify Bronsted - Lowry acids in the given reaction. Who are the experts.
Enter Friends Emails. First lets find the pOH. Identify the Bronsted-Lowry acid in the following reaction.
And the carbonic acid D can lose a proton to give bicarbonate ion B. Challenge yourself with quiz questions on the following. A NO 2 H2O HNO2 OH NO 2 H 2 O HNO 2 OH.
Using the following diagrams. According to the theory Bronsted-Lowry acid is a proton H donor and Bronsted-Lowry base is a proton H acceptor. Because water accepts a proton from water is acting as a Brønsted-Lowry base.
This means H Cl acts as an acid and H 2O acts as a base. CH3CH2COOHaq H2Ol --- CH3CH2COOaq H3Oaq The key to idenitifying Bronsted-Lowry acid-base pair and realizing that acid and base must differ in only one Hydrogen.
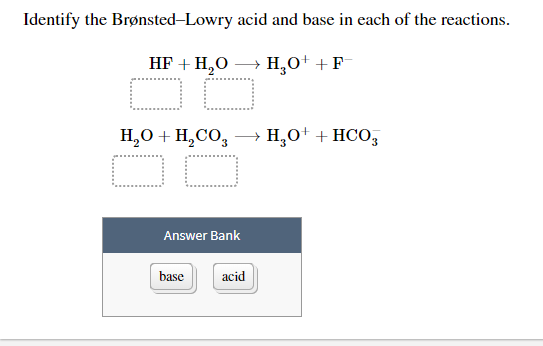
Solved Identify The Bronsted Lowry Acid And Base In Each Of Chegg Com
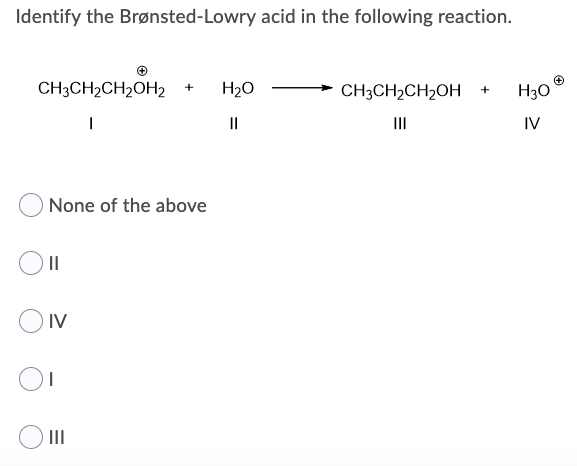
Solved Identify The Bronsted Lowry Acid In The Following Chegg Com
0 Comments